Dementia
Dementia is a brain illness that involves a deterioration in cognitive function, memory loss, and behavioral problems. It is a progressive condition that can cause severe impairment in everyday living and is frequently linked to aging. We shall explore dementia, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment choices in this website material.
What is Dementia?
Dementia is a broad term for a deterioration in cognitive function, which includes memory loss, reasoning, and problem-solving abilities. It is not a single disease but a collection of symptoms impairing the brain’s capacity to operate normally. Dementia is a progressive disease, meaning symptoms will develop with time.
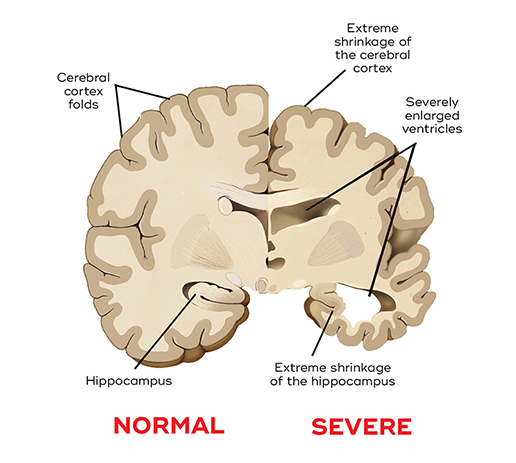
What Causes Dementia?
Alzheimer’s disease is the most frequent cause of dementia, accounting for 60-80% of cases. Other factors include:
- Vascular Dementia is characterized by a drop in blood flow to the brain.
- Lewy Body Dementia is caused by unusual protein accumulation in the brain.
- Frontotemporal Dementia is caused by damage to the brain’s frontal and temporal lobes.
- A mixture of two or more kinds of dementia is called Mixed Dementia.
Dementia Symptoms
The symptoms of dementia are based on the type of dementia and the stage of an individual’s illness. Among the most prevalent symptoms are:
- Memory Loss
- Difficulty in Communicating & Speech
- Mood & Behavioral Changes
- Difficulty Doing Daily Tasks
- Perplexity & Disoriented
- Difficulty in Problem-solving & Decision-making
Dementia is normally diagnosed using a combination of medical and neurological examinations, cognitive testing, and brain imaging. Our neurology experts also accumulate blood tests to rule out other illnesses causing symptoms.
Treatment
There is no cure for dementia, although specific medications can help control symptoms and stop the condition’s onset. For example, exercise and a nutritious diet can also help enhance general health and well-being.
Aside from medicine and lifestyle modifications, various treatment options are available to those with dementia. These are some examples:
- Rehabilitation and Cognitive Training
- Occupational Therapy (OT)
- Speech Therapy
- Art & Music Therapy
- Groups of Support
Dementia is a complicated disorder that affects millions of individuals throughout the world. While there is no cure, therapies exist to control symptoms and improve the overall quality of life. Suppose you or a loved one is experiencing dementia symptoms. In that case, seeking medical help as soon as possible is critical to acquire an accurate diagnosis and begin treatment.
OPEN HOURS
-
Artemin Hospital Sector 51, Gurugram, Haryana - 122001
- Mon - Sat 12pm to 5pm
-
Artemis life Hospital, New Friends Colony, New Delhi
- Wednesday - 4pm to 7pm
-
Medharbour Hospital, Sector 51, Gurgugram
- Mon - Thu 5pm to 7pm
For Appointment
-
Artemin Hospital Sector 51, Gurugram, Haryana - 122001
- 9910094615
-
Artemis life Hospital, New Friends Colony, New Delhi
- 01146583333/ 9818718658
-
Medharbour Hospital, Sector 51, Gurgugram
- 9971679666/ 9971631222/ 01242577222
- Copyright 2023 Dr. Sumit Singh. All Rights Reserved.
