Stroke
What is stroke (brain attack) and why should I know about it?
A stroke occurs due to brain damage because of decrease in blood supply to brain because of a blockage in the blood vessel feeding the brain. Sometimes it occurs when a blood vessel bursts, leading to bleeding in the brain. Just as heart attack which occurs due to decrease in blood supply to heart, stroke is a very serious condition and is also referred to as “brain attack”.
Is stroke (brain attack) an emergency?
If treatment is not started early enough in a brain attack patient, brain damage may be very severe. Every minute approximately two million neurons die; therefore, time is brain and emergent measures to open the blocked artery should be undertaken. New treatments are available which can significantly reduce the damage. However, these treatments work best soon after the brain attack.
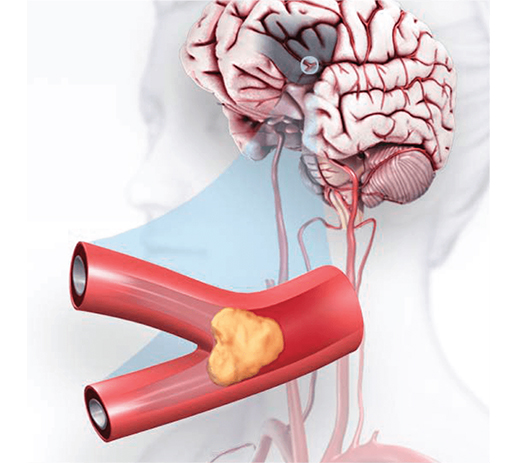
What causes stroke (brain attack)?
- “Ischaemic” brain attack is caused by decreased supply to brain due to blockage of artery supplying blood to the brain. This blockage may occur because of clot forming somewhere n the body floating into brain arteries and causing obstruction. It can also occur because of narrowing in the arteries giving blood supply to the brain.
- “Haemorrhagic” brain attack occurs due to bleeding in the brain due to hypertension, rupture of aneurysms (areas of swelling in the blood vessels), vascular malformations (areas of malformed blood vessels with increased flow in them) and many other causes.
What are the risk factors of stroke (Brain attack)?
Risk factors which one can’t modify :-
- Age- older you are, higher is the risk.
- Gender- males are more likely to have stroke.
- Race- Asians including Indians are more prone to stroke than western populations.
- Family history of stroke and heart disease.
- Hypertension- blood pressure more than 140/90 mmHg increases the risk for attack significantly. Infact hypertension is called the “silent killer”.
- Heart disease- diseases like atrial fibrillation and other disorders increase the risk.
- Carotid artery disease- carotid arteries supply blood to brain and its narrowing can predispose to brain attack.
- High cholesterol level- increases the risk.
- Smoking- smokers have higher risk, which decrease when one stops smoking.
- Diabetes- increases the risk, should be controlled by diet, oral drugs or insulin.
- Obesity- too much of weight, particularly around the waist.
- Illegal drugs- intravenous drug abuse, cocaine abuse increase the risk.
- Physical inactivity.
How do I know someone or myself is having stroke (brain attack)?
- Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm, leg (especially on one side of the body).
- Sudden confusion, trouble speaking or understanding speech.
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes.
- Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination.
- Sudden severe headache with no cause.
Tests used to diagnose brain attack
CT (Computed tomography)- this tests involve taking a series of images of the brain to detect stroke (brain attack). This test is usually the first investigation to be performed and is particularly useful to look for presence for bleeding (haemorrhagic brain attack). MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging)- This is very specialized test which uses magnetic properties of body to create very detailed images of brain as well as of blood vessels so as to diagnose brain attack.
DSA- digital subtraction angiography)- This is the most accurate in diagnosis of most of the diseases of blood vessel. A small tube (catheter) is guided from the leg blood vessel in to the blood vessel we wish to study followed by dye (contrast) injections to obtain the images. CT/MR angiography is also an option in some cases.
Doppler ultrasound: in this ultrasound method is used to image the blood vessels and the abnormalities in them.
DSA- digital subtraction angiography)- This is the most accurate in diagnosis of most of the diseases of blood vessel. A small tube (catheter) is guided from the leg blood vessel in to the blood vessel we wish to study followed by dye (contrast) injections to obtain the images. CT/MR angiography is also an option in some cases.
Doppler ultrasound: in this ultrasound method is used to image the blood vessels and the abnormalities in them.
Specialists involved in treatment of stroke
- Stroke Neurologist- specializes in evaluating and medically managing ischaemic and certain types of haemorrhagic strokes.
- Interventional neuroradiologist – specializes in minimally invasive treatment of brain attack, such as carotid stenosis stenting, intra-arterial thrombolysis, aneurysm embolization/coiling, arteriovenous malformation embolization/gluing.
- Neurosurgeon- performs surgical treatments such as hematoma evacuation, aneurysm clipping or arteriovenous malformation excision.
- Daignostic neuroradiologist- specializes in diagnosis of brain attack using modalities such as CT, MRI, Doppler etc.
What are treatment options in stroke (brain attack)?
Brain attack due to decreased blood supply (ischaemic stroke) Patients are given anti-platelet drugs, which act as “blood thinners” so as to prevent clot formation. If patient reaches early enough to a hospital with acute stroke units, they can be given thrombolytic drugs which act as clot busters and open up the blockage in the arteries so as to save as much of brain as possible. The narrowing in the arteries which have caused stroke can also be opened up by surgical or endovascular means. Brain attack due to bleeding in the brain (haemorrhagic stroke) Treatment options will depend upon the cause and size of haemorrhage. Some patients may need surgery to remove the clot, while other cases may need to be managed conservatively in ICU. Patient with bleeding due to swelling in blood vessels of brain known as “aneurysms’, will need to undergo repair of these swelling because they have a high tendency to rebleed.
Specialized minimally invasive treatments of brain attack (ischemic stroke attack)
Carotid Artery Angioplasty/Stenting: Carotid artery is a blood vessel which supplies blood to brain and its narrowing can result in brain attack. The narrowing can be treated by opening it up with a balloon followed by placing a metal mesh scaffolding (stent) across it. This is proven to be more effective than medical treatment alone in reducing the risk. This is performed early (< 2 weeks) after a minor attack to prevent a further disabling stroke.
Intravenous/Intrarterial Thrombolysis: Brain attack caused by decreased blood supply to brain can be treated by giving drugs which can open up the blockade so as to save as much of the brain as possible. These drugs can be given by intravenous route if a patient comes to the hospital within & 5 hours of onset of brain attack. These drugs can also be precisely given with in the area of blockade by placing a catheter (a small tube) from one of the leg blood vessels in to the blocked vessel. This selective (intra-arterial) treatment can be given at least up to 6-hours after the brain attack.
New Evidence Mechanical Thrombectomy: Mechanical thrombectomy is now strongly recommended for patients in whom large arteries within the brain are blocked. To open the blocked artery, doctors thread a catheter through the groin artery to the occlusion site in the brain. The stent (wired-caged device ) opens and rabs the clot, allowing doctors to remove the stent with the trapped clot. Special suction tubes may also be used. The procedure should be done within six hours of acute stroke symptoms. In > 80% of patients, the blockage can be opened and flow in the artery be established with this treatment. Approximately 60% of patients will have good recovery and be independent at 3 months.
Intravenous/Intrarterial Thrombolysis: Brain attack caused by decreased blood supply to brain can be treated by giving drugs which can open up the blockade so as to save as much of the brain as possible. These drugs can be given by intravenous route if a patient comes to the hospital within & 5 hours of onset of brain attack. These drugs can also be precisely given with in the area of blockade by placing a catheter (a small tube) from one of the leg blood vessels in to the blocked vessel. This selective (intra-arterial) treatment can be given at least up to 6-hours after the brain attack.
New Evidence Mechanical Thrombectomy: Mechanical thrombectomy is now strongly recommended for patients in whom large arteries within the brain are blocked. To open the blocked artery, doctors thread a catheter through the groin artery to the occlusion site in the brain. The stent (wired-caged device ) opens and rabs the clot, allowing doctors to remove the stent with the trapped clot. Special suction tubes may also be used. The procedure should be done within six hours of acute stroke symptoms. In > 80% of patients, the blockage can be opened and flow in the artery be established with this treatment. Approximately 60% of patients will have good recovery and be independent at 3 months.
How do you assess for salvageable tissue? What is penumbra zone?
When blood flow to the brain stops, brain cells are deprived of oxygen and nutrients. Stroke is a medical emergency because brain cells start dying quickly and the treatment is most effective when given promptly. Although some of the cells die within few minutes, surrounding zone though hypoperfused but are receiving just enough oxygen from cerebral blood flow (CBF) to stay alive. A compromised cell can survive for several hours in a low-energy state and is referred to as “penumbra”. If blood flow is restored within this narrow window of opportunity then some of these cells can be salvaged and become functional again. Blood flow to these cells can be achieved by administrating the clot-dissolving thrombolytic agent t-PA by intravenous and intra-arterial routes.
How do you assess for salvageable tissue? What is penumbra zone?
Stroke centre- is a hospital or part of a hospital that (nearly) exclusively takes care of stroke patients with specialized staff with team approach to treatment and care. Care in stroke teams (including neurologists, neurosurgeons, interventional and diagnostic neuroradiologists) or by stroke units improve the outcome in these patients significantly.
There is 24/7 access to the following at a comprehensive stroke care center:
There is 24/7 access to the following at a comprehensive stroke care center:
- 24/7 advanced imaging techniques (MRI/MRA, CTA, DSA).
- Doctors with expertise in vascular neurology, interventional neuroradiology and neurosurgery.
- 24/7 availability of personnel, imaging, operating room and endovascular facilities.
- Neuro-intensive care unit.
- Experience and expertise in treating patients with large ischemic strokes, intracerebral hemorrhage and subarachnoid hemorrhage Care in stroke teams (including neurologists, neurosurgeons, interventional and diagnostic neuroradiologists) or by stroke units improve the outcome in these patients significantly.
- Cerebrovascular lab – Trancranial dopller study for a real time assessment of blood flow, cerebrovascular reserve and monitoring for small clots.
- Patient outcomes are significantly better when they get treated at comprehensive stroke care centers.
What is the role of mechanical means of re-vascularziation in acute stroke ?
One of the disadvantages of using thrombolytic drugs is that there is risk of bleeding. Another issue is that in large vessel blockage thrombolytic drug is not effective. These drugs cannot be used in many situation such as recent surgery. To avoid these problems, mechanical means can be used to takeout the clot and open up the blocked brain blood vessel. One such device is retriever. To open the blocked artery, doctors thread a catheter through the groin artery to the occlusion site in the brain. The stent (wired-caged device ) opens and grabs the clot, allowing doctors to remove the stent with the trapped clot.
OPEN HOURS
-
Artemin Hospital Sector 51, Gurugram, Haryana - 122001
- Mon - Sat 12pm to 5pm
-
Artemis life Hospital, New Friends Colony, New Delhi
- Wednesday - 4pm to 7pm
-
Medharbour Hospital, Sector 51, Gurgugram
- Mon - Thu 5pm to 7pm
For Appointment
-
Artemin Hospital Sector 51, Gurugram, Haryana - 122001
- 9910094615
-
Artemis life Hospital, New Friends Colony, New Delhi
- 01146583333/ 9818718658
-
Medharbour Hospital, Sector 51, Gurgugram
- 9971679666/ 9971631222/ 01242577222
- Copyright 2023 Dr. Sumit Singh. All Rights Reserved.
